… A Fox host said this weekend that more Americans need to buy artificial Christmas trees because tree farms are needed for AI data centers: “There will be transmission lines that have to go through developments and farms. That’s the nature of a growing economy. Everybody needs to get on board. Buy a fake tree.” (Meidas)
I live in northern Michigan. Michigan is the third highest producer of Christmas trees in the U.S., harvesting around 2 million trees each year. We have over 500 tree farms, most concentrated in the upper half of the Mitten.
Friends of mine, growing up, had low-paying summer jobs trimming the little firs and pines into their eventual iconic triangle shapes. It’s a crappy job in early summer—dangerous and scratchy—but hey. Lots of teenagers have crappy jobs. It’s America.
I have never had an artificial tree. Some of my best friends, as the saying goes, have beautiful artificial trees, for all kinds of reasons—convenience, cleanliness, allergies—and I am seriously Not Judging.
But learning from Fox News that I should buy an artificial tree—presumably to make tree farming, a local industry, fail so that the devalued land could be looted for an AI data center—made my holiday blood boil.
Tree farms—like this one—do not despoil the rolling, wooded terrain of northern Michigan, unlike AI data centers. Most are family businesses, employing local people, investing for decades in trimming and watering, for an annual end-of-year payoff. Unlike AI data centers.
As it happens, a proposed AI Data Center in nearby Kalkaska was withdrawn after resistance to the project was quickly organized. I was surprised—Kalkaska is the quintessential up-north town, with pine-paneled bars and pot shops as the main business thrust, plus a giant trout fountain in the middle of town.
You’d think they’d jump at the chance to build a huge data factory—construction jobs in an uncertain economy when unemployment is rising? But no. They knew that “the nature of a growing economy” was going to come back to bite them with ugly power lines, jacked-up utility prices and the loss of 1500 acres of state-owned land.
When Fox News decides that fake trees are patriotic, urging us to buy plastic trees mostly made in China, to support the modern economy, something is very wrong.
But you already knew that.
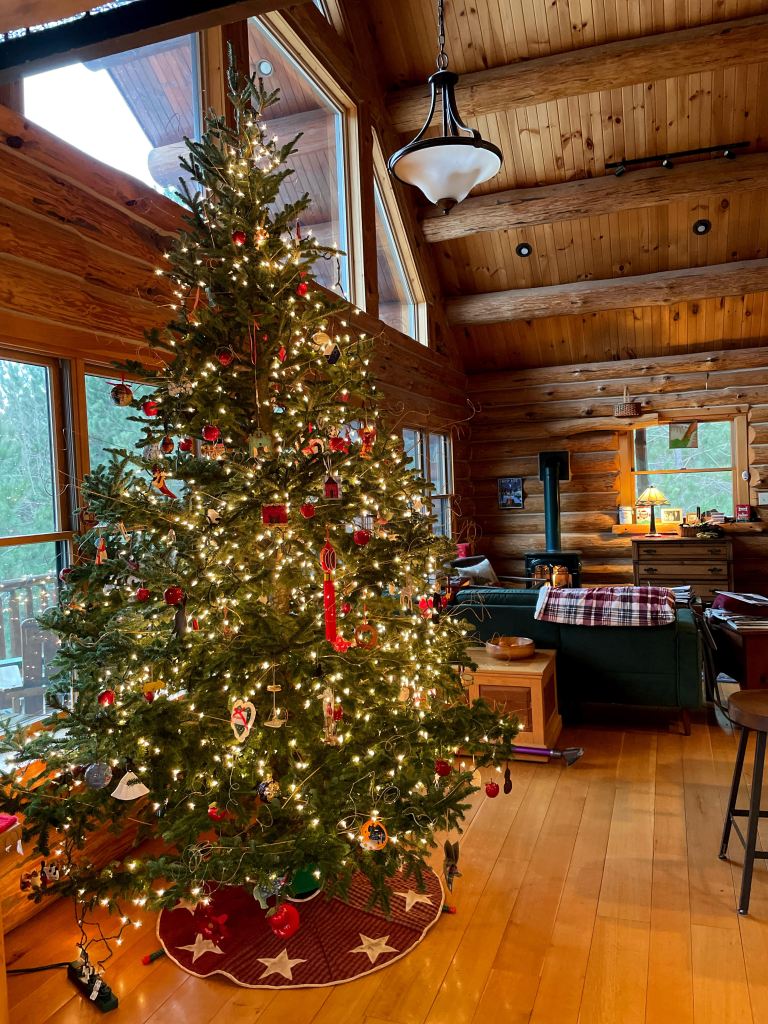
We have purchased beautiful live trees from three different local sources—two of which have gone out of business in the past decade. We are scaling back this year, with a 9-foot Fraser Fir (the photo, a 12-foot Fraser, is from two years ago). Neither of us wants to get on anything higher than a stepstool anymore.
The tree cost $60, a $10 increase over last year, with the elderly, babushka-ed lady at the cash register apologizing to each and every customer. They have to charge more, she says, to stay in business. There are lots of post-teens working—hard—in the miserable cold, probably the same ones who had summer jobs trimming trees with machetes.
Our tree was cut less than 24 hours before we took it home, bundled and tied into the back of our pickup by those same local guys. It can eventually be chipped into mulch. It smells nice.
Best of all, it’s a subtle strike-back at the wave of Artificial “Intelligence” rolling toward us.
O Tannenbaum. Wie Treu sind deine Blatter.
Happy Holidays to all Teacher in a Strange Land readers.